Customizing CI/CD with custom pipelines
Introduction
One of the core tenets of dbt is that analytic code should be version controlled. This provides a ton of benefit to your organization in terms of collaboration, code consistency, stability, and the ability to roll back to a prior version. There’s an additional benefit that is provided with your code hosting platform that is often overlooked or underutilized. Some of you may have experience using dbt Cloud’s webhook functionality to run a job when a PR is created. This is a fantastic capability, and meets most use cases for testing your code before merging to production. However, there are circumstances when an organization needs additional functionality, like running workflows on every commit (linting), or running workflows after a merge is complete. In this article, we will show you how to setup custom pipelines to lint your project and trigger a dbt Cloud job via the API.
A note on parlance in this article since each code hosting platform uses different terms for similar concepts. The terms pull request (PR) and merge request (MR) are used interchangeably to mean the process of merging one branch into another branch.
What are pipelines?
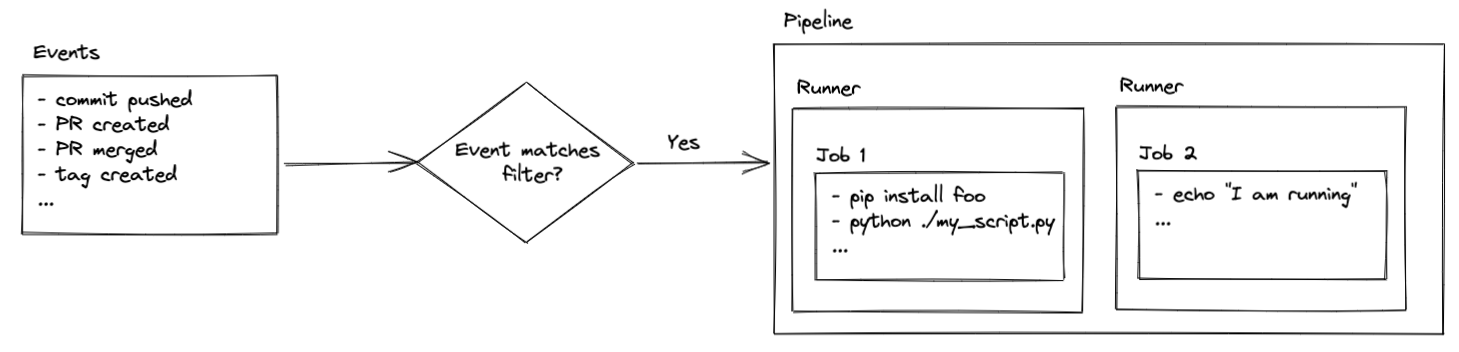
Pipelines (which are known by many names, such as workflows, actions, or build steps) are a series of pre-defined jobs that are triggered by specific events in your repository (PR created, commit pushed, branch merged, etc). Those jobs can do pretty much anything your heart desires assuming you have the proper security access and coding chops.
Jobs are executed on runners, which are virtual servers. The runners come pre-configured with Ubuntu Linux, macOS, or Windows. That means the commands you execute are determined by the operating system of your runner. You’ll see how this comes into play later in the setup, but for now just remember that your code is executed on virtual servers that are, typically, hosted by the code hosting platform.
Please note, runners hosted by your code hosting platform provide a certain amount of free time. After that, billing charges may apply depending on how your account is setup. You also have the ability to host your own runners. That is beyond the scope of this article, but checkout the links below for more information if you’re interested in setting that up:
- Repo-hosted runner billing information:
- Self-hosted runner information:
Additionally, if you’re using the free tier of GitLab you can still follow this guide, but it may ask you to provide a credit card to verify your account. You’ll see something like this the first time you try to run a pipeline:
How to setup pipelines
This guide provides details for multiple code hosting platforms. Where steps are unique, they are presented without a selection option. If code is specific to a platform (i.e. GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) you will see a selection option for each.
Pipelines can be triggered by various events. The dbt Cloud webhook process already triggers a run if you want to run your jobs on a merge request, so this guide focuses on running pipelines for every push and when PRs are merged. Since pushes happen frequently in a project, we’ll keep this job super simple and fast by linting with SQLFluff. The pipeline that runs on merge requests will run less frequently, and can be used to call the dbt Cloud API to trigger a specific job. This can be helpful if you have specific requirements that need to happen when code is updated in production, like running a --full-refresh on all impacted incremental models.
Here’s a quick look at what this pipeline will accomplish:
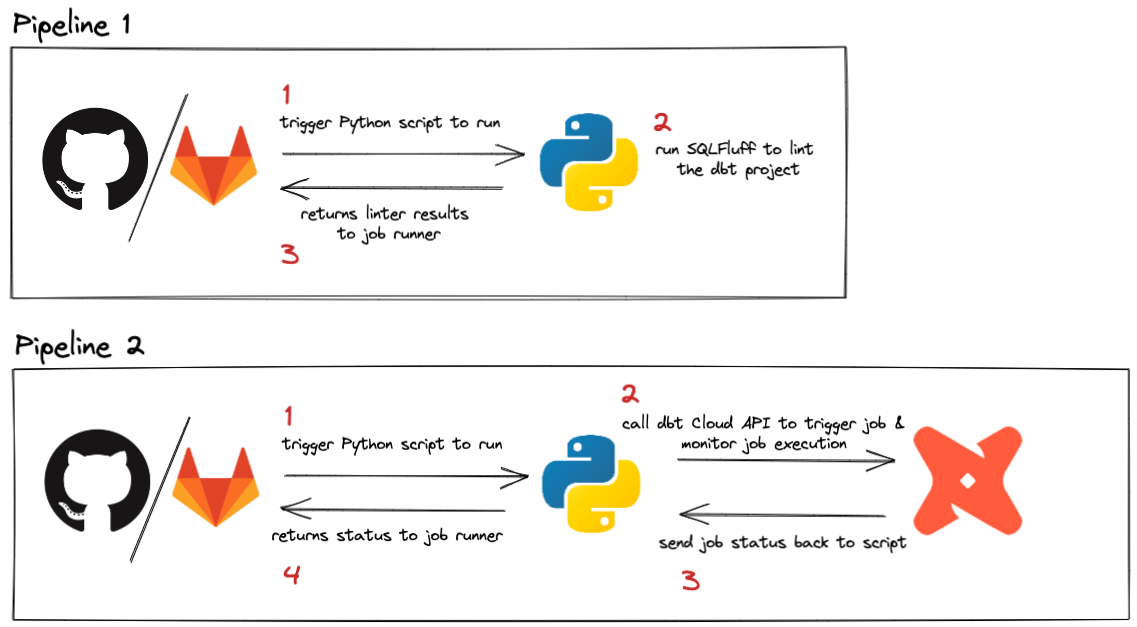
Run a dbt Cloud job on merge
This job will take a bit more to setup, but is a good example of how to call the dbt Cloud API from a CI/CD pipeline. The concepts presented here can be generalized and used in whatever way best suits your use case.
If your Git provider has a native integration with dbt Cloud, you can take advantage of setting up Merge jobs in the UI.
The setup below shows how to call the dbt Cloud API to run a job every time there's a push to your main branch (The branch where pull requests are typically merged. Commonly referred to as the main, primary, or master branch, but can be named differently).
1. Get your dbt Cloud API key
When running a CI/CD pipeline you’ll want to use a service token instead of any individual’s API key. There are detailed docs available on this, but below is a quick rundown (this must be performed by an Account Admin):
- Login to your dbt Cloud account
- In the upper left, click the menu button, then Account Settings
- Click Service Tokens on the left
- Click New Token to create a new token specifically for CI/CD API calls
- Name your token something like “CICD Token”
- Click the +Add button under Access, and grant this token the Job Admin permission
- Click Save and you’ll see a grey box appear with your token. Copy that and save it somewhere safe (this is a password, and should be treated as such).
Here’s a video showing the steps as well:
2. Put your dbt Cloud API key into your repo
This next part will happen in you code hosting platform. We need to save your API key from above into a repository secret so the job we create can access it. It is not recommended to ever save passwords or API keys in your code, so this step ensures that your key stays secure, but is still usable for your pipelines.
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Azure DevOps
- Bitbucket
- Open up your repository where you want to run the pipeline (the same one that houses your dbt project)
- Click Settings to open up the repository options
- On the left click the Secrets and variables dropdown in the Security section
- From that list, click on Actions
- Towards the middle of the screen, click the New repository secret button
- It will ask you for a name, so let’s call ours
DBT_API_KEY- It’s very important that you copy/paste this name exactly because it’s used in the scripts below.
- In the Secret section, paste in the key you copied from dbt Cloud
- Click Add secret and you’re all set!
** A quick note on security: while using a repository secret is the most straightforward way to setup this secret, there are other options available to you in GitHub. They’re beyond the scope of this guide, but could be helpful if you need to create a more secure environment for running actions. Checkout GitHub’s documentation on secrets here.*
Here’s a video showing these steps:
-
Open up your repository where you want to run the pipeline (the same one that houses your dbt project)
-
Click Settings > CI/CD
-
Under the Variables section, click Expand, then click Add variable
-
It will ask you for a name, so let’s call ours
DBT_API_KEY- It’s very important that you copy/paste this name exactly because it’s used in the scripts below.
-
In the Value section, paste in the key you copied from dbt Cloud
-
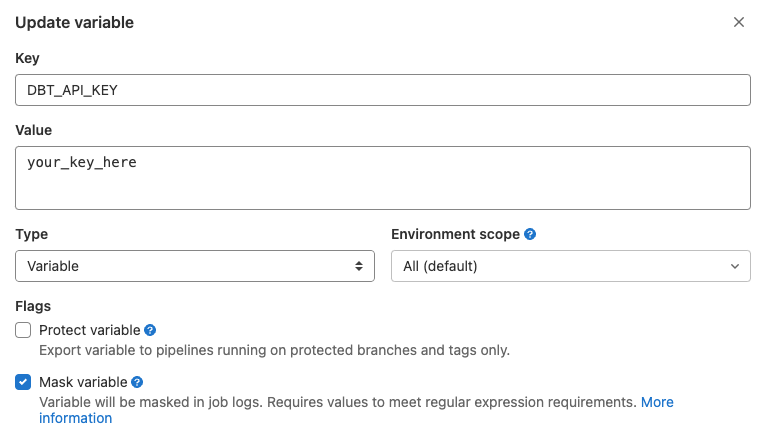
Make sure the check box next to Protect variable is unchecked, and the box next to Mask variable is selected (see below)
- “Protected” means that the variable is only available in pipelines that run on protected branches or protected tags - that won’t work for us because we want to run this pipeline on multiple branches. “Masked” means that it will be available to your pipeline runner, but will be masked in the logs.
Here’s a video showing these steps:
In Azure:
- Open up your Azure DevOps project where you want to run the pipeline (the same one that houses your dbt project)
- Click on Pipelines and then Create Pipeline
- Select where your git code is located. It should be Azure Repos Git
- Select your git repository from the list
- Select Starter pipeline (this will be updated later in Step 4)
- Click on Variables and then New variable
- In the Name field, enter the
DBT_API_KEY- It’s very important that you copy/paste this name exactly because it’s used in the scripts below.
- In the Value section, paste in the key you copied from dbt Cloud
- Make sure the check box next to Keep this value secret is checked. This will mask the value in logs, and you won't be able to see the value for the variable in the UI.
- Click OK and then Save to save the variable
- Save your new Azure pipeline
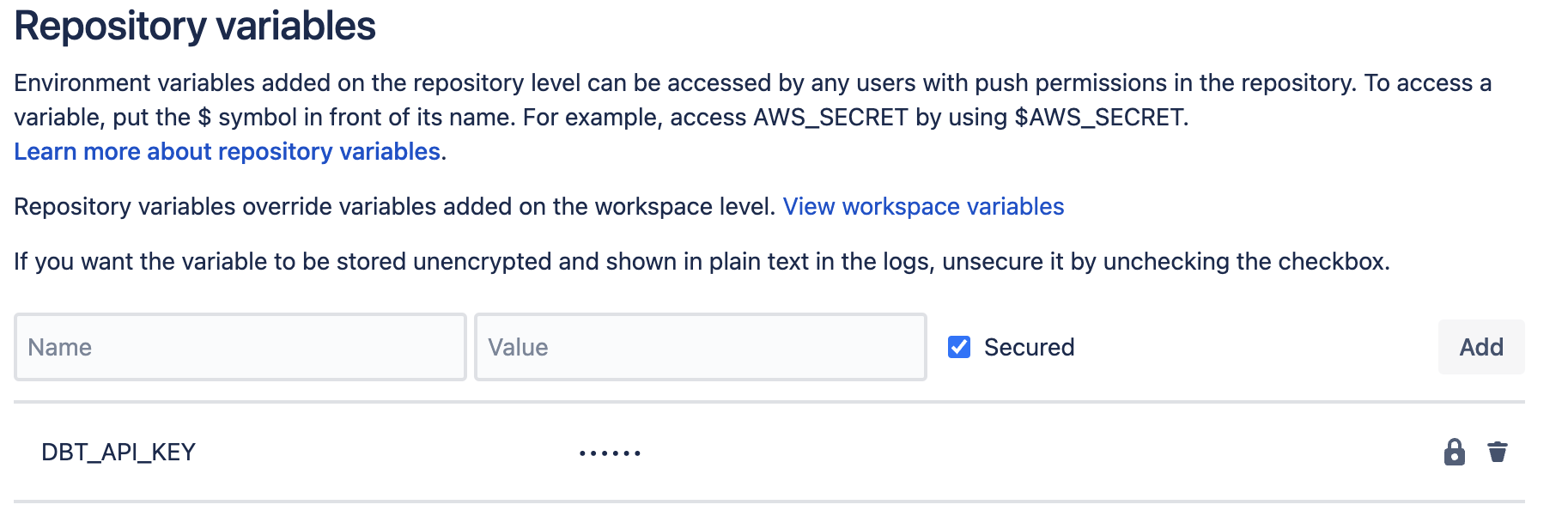
In Bitbucket:
-
Open up your repository where you want to run the pipeline (the same one that houses your dbt project)
-
In the left menu, click Repository Settings
-
Scroll to the bottom of the left menu, and select Repository variables
-
In the Name field, input
DBT_API_KEY- It’s very important that you copy/paste this name exactly because it’s used in the scripts below.
-
In the Value section, paste in the key you copied from dbt Cloud
-
Make sure the check box next to Secured is checked. This will mask the value in logs, and you won't be able to see the value for the variable in the UI.
-
Click Add to save the variable
Here’s a video showing these steps:
3. Create script to trigger dbt Cloud job via an API call
In your dbt Cloud project, create a new folder at the root level named python. In that folder, create a file named run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py. You’ll copy/paste the contents from this gist into that file.
my_awesome_project
├── python
│ └── run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
This Python file has everything you need to call the dbt Cloud API, but requires a few inputs (see snip below). Those inputs are fed to this script through environment variables that will be defined in the next step.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# get environment variables
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
api_base = os.getenv('DBT_URL', 'https://cloud.getdbt.com/') # default to multitenant url
job_cause = os.getenv('DBT_JOB_CAUSE', 'API-triggered job') # default to generic message
git_branch = os.getenv('DBT_JOB_BRANCH', None) # default to None
schema_override = os.getenv('DBT_JOB_SCHEMA_OVERRIDE', None) # default to None
api_key = os.environ['DBT_API_KEY'] # no default here, just throw an error here if key not provided
account_id = os.environ['DBT_ACCOUNT_ID'] # no default here, just throw an error here if id not provided
project_id = os.environ['DBT_PROJECT_ID'] # no default here, just throw an error here if id not provided
job_id = os.environ['DBT_PR_JOB_ID'] # no default here, just throw an error here if id not provided
Required input:
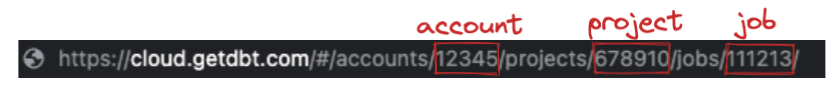
In order to call the dbt Cloud API, there are a few pieces of info the script needs. The easiest way to get these values is to open up the job you want to run in dbt Cloud. The URL when you’re inside the job has all the values you need:
DBT_ACCOUNT_ID- this is the number just afteraccounts/in the URLDBT_PROJECT_ID- this is the number just afterprojects/in the URLDBT_PR_JOB_ID- this is the number just afterjobs/in the URL
4. Update your project to include the new API call
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Azure DevOps
- Bitbucket
For this new job, we’ll add a file for the dbt Cloud API call named dbt_run_on_merge.yml.
my_awesome_project
├── python
│ └── run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
├── .github
│ ├── workflows
│ │ └── dbt_run_on_merge.yml
│ │ └── lint_on_push.yml
The YAML file will look pretty similar to our earlier job, but there is a new section called env that we’ll use to pass in the required variables. Update the variables below to match your setup based on the comments in the file.
It’s worth noting that we changed the on: section to now run only when there are pushes to a branch named main (i.e. a PR is merged). Have a look through GitHub’s docs on these filters for additional use cases.
name: run dbt Cloud job on push
# This filter says only run this job when there is a push to the main branch
# This works off the assumption that you've restricted this branch to only all PRs to push to the default branch
# Update the name to match the name of your default branch
on:
push:
branches:
- 'main'
jobs:
# the job calls the dbt Cloud API to run a job
run_dbt_cloud_job:
name: Run dbt Cloud Job
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Set the environment variables needed for the run
env:
DBT_ACCOUNT_ID: 00000 # enter your account id
DBT_PROJECT_ID: 00000 # enter your project id
DBT_PR_JOB_ID: 00000 # enter your job id
DBT_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.DBT_API_KEY }}
DBT_JOB_CAUSE: 'GitHub Pipeline CI Job'
DBT_JOB_BRANCH: ${{ github.ref_name }}
steps:
- uses: "actions/checkout@v4"
- uses: "actions/setup-python@v5"
with:
python-version: "3.9"
- name: Run dbt Cloud job
run: "python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py"
For this job, we'll set it up using the gitlab-ci.yml file as in the prior step (see Step 1 of the linting setup for more info). The YAML file will look pretty similar to our earlier job, but there is a new section called variables that we’ll use to pass in the required variables to the Python script. Update this section to match your setup based on the comments in the file.
Please note that the rules: section now says to run only when there are pushes to a branch named main, such as a PR being merged. Have a look through GitLab’s docs on these filters for additional use cases.
- Only dbt Cloud job
- Lint and dbt Cloud job
image: python:3.9
variables:
DBT_ACCOUNT_ID: 00000 # enter your account id
DBT_PROJECT_ID: 00000 # enter your project id
DBT_PR_JOB_ID: 00000 # enter your job id
DBT_API_KEY: $DBT_API_KEY # secret variable in gitlab account
DBT_URL: https://cloud.getdbt.com
DBT_JOB_CAUSE: 'GitLab Pipeline CI Job'
DBT_JOB_BRANCH: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH
stages:
- build
# this job calls the dbt Cloud API to run a job
run-dbt-cloud-job:
stage: build
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == 'main'
script:
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
image: python:3.9
variables:
DBT_ACCOUNT_ID: 00000 # enter your account id
DBT_PROJECT_ID: 00000 # enter your project id
DBT_PR_JOB_ID: 00000 # enter your job id
DBT_API_KEY: $DBT_API_KEY # secret variable in gitlab account
DBT_URL: https://cloud.getdbt.com
DBT_JOB_CAUSE: 'GitLab Pipeline CI Job'
DBT_JOB_BRANCH: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH
stages:
- pre-build
- build
# this job runs SQLFluff with a specific set of rules
# note the dialect is set to Snowflake, so make that specific to your setup
# details on linter rules: https://docs.sqlfluff.com/en/stable/rules.html
lint-project:
stage: pre-build
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH != 'main'
script:
- python -m pip install sqlfluff==0.13.1
- sqlfluff lint models --dialect snowflake --rules L019,L020,L021,L022
# this job calls the dbt Cloud API to run a job
run-dbt-cloud-job:
stage: build
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == 'main'
script:
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
For this new job, open the existing Azure pipeline you created above and select the Edit button. We'll want to edit the corresponding Azure pipeline YAML file with the appropriate configuration, instead of the starter code, along with including a variables section to pass in the required variables.
Copy the below YAML file into your Azure pipeline and update the variables below to match your setup based on the comments in the file. It's worth noting that we changed the trigger section so that it will run only when there are pushes to a branch named main (like a PR merged to your main branch).
Read through Azure's docs on these filters for additional use cases.
name: Run dbt Cloud Job
trigger: [ main ] # runs on pushes to main
variables:
DBT_URL: https://cloud.getdbt.com # no trailing backslash, adjust this accordingly for single-tenant deployments
DBT_JOB_CAUSE: 'Azure Pipeline CI Job' # provide a descriptive job cause here for easier debugging down the road
DBT_ACCOUNT_ID: 00000 # enter your account id
DBT_PROJECT_ID: 00000 # enter your project id
DBT_PR_JOB_ID: 00000 # enter your job id
steps:
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.7'
displayName: 'Use Python 3.7'
- script: |
python -m pip install requests
displayName: 'Install python dependencies'
- script: |
python -u ./python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
displayName: 'Run dbt job '
env:
DBT_API_KEY: $(DBT_API_KEY) # Set these values as secrets in the Azure pipelines Web UI
For this job, we'll set it up using the bitbucket-pipelines.yml file as in the prior step (see Step 1 of the linting setup for more info). The YAML file will look pretty similar to our earlier job, but we’ll pass in the required variables to the Python script using export statements. Update this section to match your setup based on the comments in the file.
- Only dbt Cloud job
- Lint and dbt Cloud job
image: python:3.11.1
pipelines:
branches:
'main': # override if your default branch doesn't run on a branch named "main"
- step:
name: 'Run dbt Cloud Job'
script:
- export DBT_URL="https://cloud.getdbt.com" # if you have a single-tenant deployment, adjust this accordingly
- export DBT_JOB_CAUSE="Bitbucket Pipeline CI Job"
- export DBT_ACCOUNT_ID=00000 # enter your account id here
- export DBT_PROJECT_ID=00000 # enter your project id here
- export DBT_PR_JOB_ID=00000 # enter your job id here
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
image: python:3.11.1
pipelines:
branches:
'**': # this sets a wildcard to run on every branch unless specified by name below
- step:
name: Lint dbt project
script:
- python -m pip install sqlfluff==0.13.1
- sqlfluff lint models --dialect snowflake --rules L019,L020,L021,L022
'main': # override if your default branch doesn't run on a branch named "main"
- step:
name: 'Run dbt Cloud Job'
script:
- export DBT_URL="https://cloud.getdbt.com" # if you have a single-tenant deployment, adjust this accordingly
- export DBT_JOB_CAUSE="Bitbucket Pipeline CI Job"
- export DBT_ACCOUNT_ID=00000 # enter your account id here
- export DBT_PROJECT_ID=00000 # enter your project id here
- export DBT_PR_JOB_ID=00000 # enter your job id here
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
5. Test your new action
Now that you have a shiny new action, it’s time to test it out! Since this change is setup to only run on merges to your default branch, you’ll need to create and merge this change into your main branch. Once you do that, you’ll see a new pipeline job has been triggered to run the dbt Cloud job you assigned in the variables section.
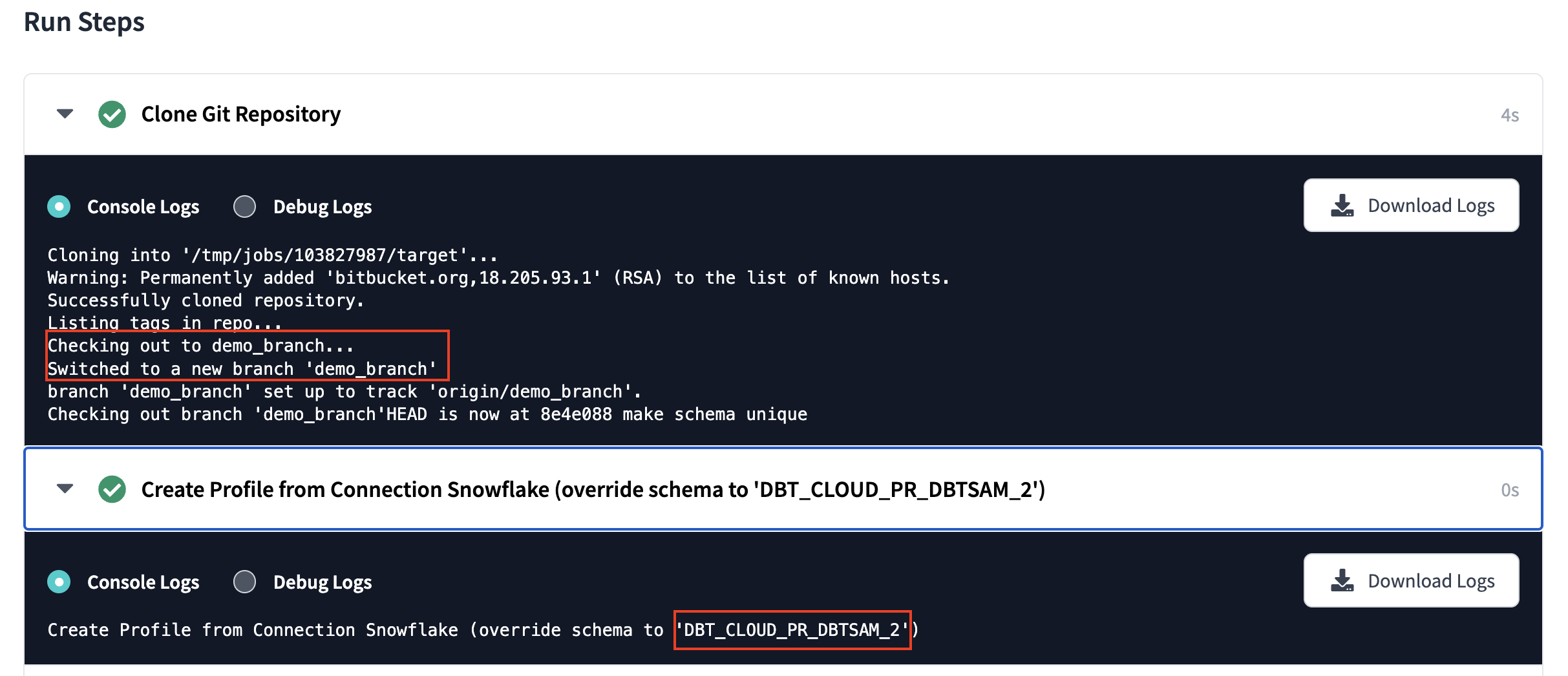
Additionally, you’ll see the job in the run history of dbt Cloud. It should be fairly easy to spot because it will say it was triggered by the API, and the INFO section will have the branch you used for this guide.
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Azure DevOps
- Bitbucket
Run a dbt Cloud job on pull request
If your git provider is not one with a native integration with dbt Cloud, but you still want to take advantage of CI builds, you've come to the right spot! With just a bit of work it's possible to setup a job that will run a dbt Cloud job when a pull request (PR) is created.
If your git provider has a native integration with dbt Cloud, you can take advantage of the setup instructions here. This section is only for those projects that connect to their git repository using an SSH key.
The setup for this pipeline will use the same steps as the prior page. Before moving on, follow steps 1-5 from the prior page.
1. Create a pipeline job that runs when PRs are created
- Bitbucket
For this job, we'll set it up using the bitbucket-pipelines.yml file as in the prior step. The YAML file will look pretty similar to our earlier job, but we’ll pass in the required variables to the Python script using export statements. Update this section to match your setup based on the comments in the file.
What is this pipeline going to do?
The setup below will trigger a dbt Cloud job to run every time a PR is opened in this repository. It will also run a fresh version of the pipeline for every commit that is made on the PR until it is merged.
For example: If you open a PR, it will run the pipeline. If you then decide additional changes are needed, and commit/push to the PR branch, a new pipeline will run with the updated code.
The following varibles control this job:
DBT_JOB_BRANCH: Tells the dbt Cloud job to run the code in the branch that created this PRDBT_JOB_SCHEMA_OVERRIDE: Tells the dbt Cloud job to run this into a custom target schema- The format of this will look like:
DBT_CLOUD_PR_{REPO_KEY}_{PR_NUMBER}
- The format of this will look like:
image: python:3.11.1
pipelines:
# This job will run when pull requests are created in the repository
pull-requests:
'**':
- step:
name: 'Run dbt Cloud PR Job'
script:
# Check to only build if PR destination is master (or other branch).
# Comment or remove line below if you want to run on all PR's regardless of destination branch.
- if [ "${BITBUCKET_PR_DESTINATION_BRANCH}" != "main" ]; then printf 'PR Destination is not master, exiting.'; exit; fi
- export DBT_URL="https://cloud.getdbt.com"
- export DBT_JOB_CAUSE="Bitbucket Pipeline CI Job"
- export DBT_JOB_BRANCH=$BITBUCKET_BRANCH
- export DBT_JOB_SCHEMA_OVERRIDE="DBT_CLOUD_PR_"$BITBUCKET_PROJECT_KEY"_"$BITBUCKET_PR_ID
- export DBT_ACCOUNT_ID=00000 # enter your account id here
- export DBT_PROJECT_ID=00000 # enter your project id here
- export DBT_PR_JOB_ID=00000 # enter your job id here
- python python/run_and_monitor_dbt_job.py
2. Confirm the pipeline runs
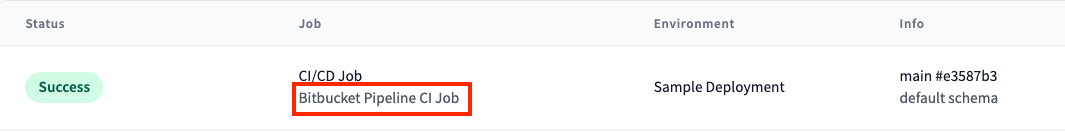
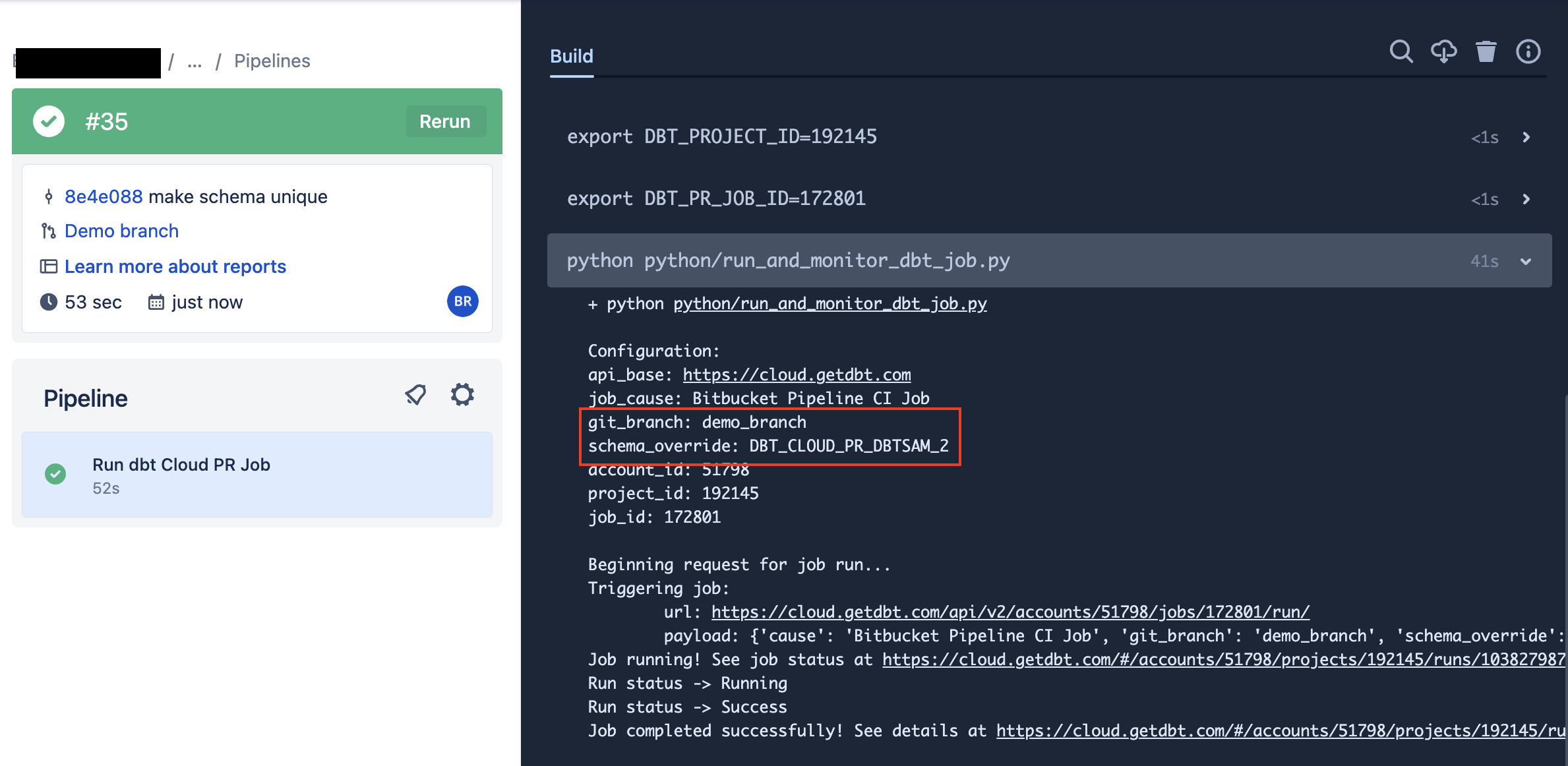
Now that you have a new pipeline, it's time to run it and make sure it works. Since this only triggers when a PR is created, you'll need to create a new PR on a branch that contains the code above. Once you do that, you should see a pipeline that looks like this:
- Bitbucket
Bitbucket pipeline:
dbt Cloud job:
3. Handle those extra schemas in your database
As noted above, when the PR job runs it will create a new schema based on the PR. To avoid having your database overwhelmed with PR schemas, consider adding a "cleanup" job to your dbt Cloud account. This job can run on a scheduled basis to cleanup any PR schemas that haven't been updated/used recently.
Add this as a macro to your project. It takes 2 arguments that lets you control which schema get dropped:
age_in_days: The number of days since the schema was last altered before it should be dropped (default 10 days)database_to_clean: The name of the database to remove schemas from
{#
This macro finds PR schemas older than a set date and drops them
The macro defaults to 10 days old, but can be configured with the input argument age_in_days
Sample usage with different date:
dbt run-operation pr_schema_cleanup --args "{'database_to_clean': 'analytics','age_in_days':'15'}"
#}
{% macro pr_schema_cleanup(database_to_clean, age_in_days=10) %}
{% set find_old_schemas %}
select
'drop schema {{ database_to_clean }}.'||schema_name||';'
from {{ database_to_clean }}.information_schema.schemata
where
catalog_name = '{{ database_to_clean | upper }}'
and schema_name ilike 'DBT_CLOUD_PR%'
and last_altered <= (current_date() - interval '{{ age_in_days }} days')
{% endset %}
{% if execute %}
{{ log('Schema drop statements:' ,True) }}
{% set schema_drop_list = run_query(find_old_schemas).columns[0].values() %}
{% for schema_to_drop in schema_drop_list %}
{% do run_query(schema_to_drop) %}
{{ log(schema_to_drop ,True) }}
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{% endmacro %}
This macro goes into a dbt Cloud job that is run on a schedule. The command will look like this (text below for copy/paste):

dbt run-operation pr_schema_cleanup --args "{ 'database_to_clean': 'development','age_in_days':15}"
Consider risk of conflicts when using multiple orchestration tools
Running dbt Cloud jobs through a CI/CD pipeline is a form of job orchestration. If you also run jobs using dbt Cloud’s built in scheduler, you now have 2 orchestration tools running jobs. The risk with this is that you could run into conflicts - you can imagine a case where you are triggering a pipeline on certain actions and running scheduled jobs in dbt Cloud, you would probably run into job clashes. The more tools you have, the more you have to make sure everything talks to each other.
That being said, if the only reason you want to use pipelines is for adding a lint check or run on merge, you might decide the pros outweigh the cons, and as such you want to go with a hybrid approach. Just keep in mind that if two processes try and run the same job at the same time, dbt Cloud will queue the jobs and run one after the other. It’s a balancing act but can be accomplished with diligence to ensure you’re orchestrating jobs in a manner that does not conflict.




?v=2)